Packages This Package Prev Next Index
§3.2 Class Date
public class java.util.Date
extends java.lang.Object (I-§1.12)
{
// Constructors
public Date(); §3.2.1
public Date(int year, int month, int date); §3.2.2
public Date(int year, int month, int date, §3.2.3
int hrs, int min);
public Date(int year, int month, int date, §3.2.4
int hrs, int min, int sec);
public Date(long date); §3.2.5
public Date(String s); §3.2.6
// Methods
public boolean after(Date when); §3.2.7
public boolean before(Date when); §3.2.8
public boolean equals(Object obj); §3.2.9
public int getDate(); §3.2.10
public int getDay(); §3.2.11
public int getHours(); §3.2.12
public int getMinutes(); §3.2.13
public int getMonth(); §3.2.14
public int getSeconds(); §3.2.15
public long getTime(); §3.2.16
public int getTimezoneOffset(); §3.2.17
public int getYear(); §3.2.18
public int hashCode(); §3.2.19
public static long parse(String s); §3.2.20
public void setDate(int date); §3.2.21
public void setHours(int hours); §3.2.22
public void setMinutes(int minutes); §3.2.23
public void setMonth(int month); §3.2.24
public void setSeconds(int seconds); §3.2.25
public void setTime(long time); §3.2.26
public void setYear(int year); §3.2.27
public String toGMTString(); §3.2.28
public String toLocaleString(); §3.2.29
public String toString(); §3.2.30
public static long UTC(int year, int month, int date, §3.2.31
int hrs, int min, int sec);
}
The class Date provides anabstraction of dates and times. Dates may be constructed from a
year, month, date (day of month), hour, minute, and second. Those six components, as
well as the day of the week, may be extracted from a date. Dates may also be compared
and converted to a readable string form. A date is represented to a precision of one millisecond.
To print today's date:
To find out the day of the week for some particular date, for example, January 16, 1963:
While the Date class is intended to reflect UTC (Coordinated Universal Time), it may not
do so exactly, depending on the host environment of the Java Virtual Machine. Nearly all
modern operating systems assume that 1 day = 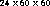 = 86400 seconds in all cases.
In UTC, however, about once every year or two there is an extra second, called a "leap
second." The leap second is always added as the last second of the day, and always on
December 31 or June 30. For example, the last minute of the year 1995 was 61 seconds
long, thanks to an added leap second. Most computer clocks are not accurate enough to be
able to reflect the leap-second distinction.
= 86400 seconds in all cases.
In UTC, however, about once every year or two there is an extra second, called a "leap
second." The leap second is always added as the last second of the day, and always on
December 31 or June 30. For example, the last minute of the year 1995 was 61 seconds
long, thanks to an added leap second. Most computer clocks are not accurate enough to be
able to reflect the leap-second distinction.
Some computer standards are defined in terms of GMT (Greenwich Mean Time), which is
equivalent to UT (Universal Time). GMT is the "civil" name for the standard; UT is the
"scientific" name for the same standard. The distinction between UTC and UT is that UTC
is based on an atomic clock and UT is based on astronomical observations, which for all
practical purposes is an invisibly fine hair to split. Because the earth's rotation is not uniform-it slows down and speeds up in complicated ways-UT does not always flow uniformly. Leap seconds are introduced as needed into UTC so as to keep UTC within 0.9
seconds of UT1, which is a version of UT with certain corrections applied. There are other
time and date systems as well; for example, the time scale used by GPS (the satellite-based
Global Positioning System) is synchronized to UTC but is not adjusted for leap seconds.
An interesting source of further information is the US Naval Observatory, particularly the
Directorate of Time at
and their definitions of "Systems of Time" at
In all methods of class Date that accept or return year, month, date, hours, minutes, and
seconds values, the following representations are used:
In all cases, arguments given to methods for these purposes need not fall within the indicated ranges; for example, a date may be specified as January 32 and is interpreted as
meaning February 1.
Date
public Date()
- Allocates a Date object and initializes it so that it represents the time at
which it was allocated measured to the nearest millisecond.
- See Also:
- currentTimeMillis (I-§1.18.5) in class System.
Date
public Date(int year, int month, int date)
- Allocates a Date object and initializes it so that it represents midnight, local
time, at the beginning of the day specified by the year, month, and date arguments.
- Parameters:
year
- the year minus 1900
month
- a month between 0-11
date
- day of the month between 1-31
Date
public Date(int year, int month, int date, int hrs, int min)
- Allocates a Date object and initializes it so that it represents the specified
hour and minute, local time, of the date specified by the year, month, and
date arguments.
- Parameters:
year
- the year minus 1900
month
- a month between 0-11
date
- day of the month between 1-31
hrs
- hours between 0-23
min
- minutes between 0-59
Date
public Date(int year, int month, int date, int hrs,
int min, int sec)
- Allocates a Date object and initializes it so that it represents the specified
hour, minute, and second, local time of the date specified by the year,
month, and date arguments.
- Parameters:
year
- the year minus 1900
month
- a month between 0-11
date
- day of the month between 1-31
hrs
- hours between 0-23
min
- minutes between 0-59
sec
- seconds between 0-59
Date
public Date(long date)
- Allocates a Date object and initializes it to represent the specified number
of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00GMT.
- Parameters:
date
- milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT
- See Also:
- currentTimeMillis (I-§1.18.5) in class System.
Date
public Date(String s)
- Allocates a Date object and initializes it that that it represents the date and
time indicated by the string s, which is interpreted as if by the parse method
(I-§3.2.20).
- Parameters:
s
- a string representation of the date.
after
public boolean after(Date when)
- Parameters:
when
- a date
- Returns:
- true if this date is after the argument date; false otherwise.
before
public boolean before(Date when)
- Parameters:
when
- a date
- Returns:
- true if this date is before the argument date; false otherwise.
equals
public boolean equals(Object obj)
- The result is true if and only if the argument is not null and is a Date object
that represents the same point in time, to the millisecond, as this object.
- Thus two Date objects are equal if and only if the getTime method
(I-§3.2.16) returns the same long value for both.
- Parameters:
obj
- the object to compare with
- Returns:
- true if the objects are the same; false otherwise.
- Overrides:
- equals in class Object (I-§1.12.3).
getDate
public int getDate()
- Returns:
- the day of the month represented by this date. The value returned is
between 1 and 31.
getDay
public int getDay()
- Returns:
- the day of the week represented by this date. The value returned is
between 0 and 6, where 0 represents Sunday.
getHours
public int getHours()
- Returns:
- the hour represented by this date. The value returned is between 0 and
23, where 0 represents midnight.
getMinutes
public int getMinutes()
- Returns:
- the number of minutes past the hour represented by this date. The
value returned is between 0 and 59.
getMonth
public int getMonth()
- Returns:
- the month represented by this date. The value returned is between 0
and 11, with the value 0 representing January.
getSeconds
public int getSeconds()
- Returns:
- the number of seconds past the minute represented by this date. The
value returned is between 0 and 60. The value 60 can only occur on
those Java Virtual Machines that take leap seconds into account.
getTime
public long getTime()
- Returns:
- the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT represented by this date.
getTimezoneOffset
public int getTimezoneOffset()
- Determines the local time zone offset. The time zone noffset is the number
of minutes that must be added to Greenwich Mean Time to give the local
time zone. This value includes the correction, if necessary, for daylight
savings time.
- Returns:
- the time zone offset, in minutes, for the current locale.
getYear
public int getYear()
- Returns:
- the year represented by this date, minus 1900.
hashCode
public int hashCode()
- Returns:
- a hash code value for this object.
- Overrides:
- hashCode in class Object (I-§1.12.6).
parse
public static long parse(String s)
- Given a string representing a time, parse it and return the time value. This
method recognizes most standard syntaxes.
- It accepts many syntaxes; in particular, it recognizes the IETF standard
date syntax: "Sat, 12 Aug 1995 13:30:00 GMT". It also understands the
continental US time zone abbreviations, but for general use, a timezone
offset should be used: "Sat, 12 Aug 1995 13:30:00 GMT+0430" (4 hours,
30 minutes west of the Greenwich meridian). If no time zone is specified,
the local time zone is assumed. GMT and UTC are considered equivalent.
- Parameters:
s
- a string to be parsed as a date
- Returns:
- the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT represented by the string argument
setDate
public void setDate(int date)
- Sets the day of the month of this date to the specified value
- Parameters:
date
- the day value
setHours
public void setHours(int hours)
- Sets the hour of this date to the specified value
- Parameters:
hours
- the hour value
setMinutes
public void setMinutes(int minutes)
- Sets the minutes of this date to the specified value
- Parameters:
minutes
- the value of the minutes
setMonth
public void setMonth(int month)
- Sets the month of this date to the specified value.
- Parameters:
month
- the month value (0-11)
setSeconds
public void setSeconds(int seconds)
- Sets the seconds of this date to the specified value.
- Parameters:
seconds
- the second value
setTime
public void setTime(long time)
- Sets this date to represent the specified number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970 00:00:00 GMT.
- Parameters:
time
- A number of milliseconds
setYear
public void setYear(int year)
- Sets the year of this date to be the specified value plus 1900.
- Parameters:
year
- the year value
toGMTString
public String toGMTString()
- Creates a string representation of this date. The result is of the form
- the day of the month is always one or two digits. The other fields have
exactly the width shown. The timezone is always given as "GMT".
- Returns:
- A string represention of this date, using the Internet GMT conventions.
toLocaleString
public String toLocaleString()
- Creates a string representation of this date is an implementation-dependent
form. The intent is that the form should be familiar to the user of the Java
application, wherever it may happen to be running. The intent is comparible to that of the %c format supported by the strftime() function of ISO C.
- Returns:
- A string representation of this date, using the locale conventions.
toString
public String toString()
- Creates a canonical string representation of the date. The result is of the
form "Sat Aug 12 02:30:00 PDT 1995".
- Returns:
- A string representation of this date.
- Overrides:
- toString in class Object (I-§1.12.9).
UTC
public static long
UTC(int year, int month, int date, int hrs, int min, int sec)
- Determines the date and time based on the arguments. The arguments are
interpreted in UTC, not in the local time zone.
- Parameters:
year
- the year minus 1900
month
- a month between 0-11
date
- day of the month between 1-31
hrs
- hours between 0-23
min
- minutes between 0-59
sec
- seconds between 0-59
- Returns:
- the number of seconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT for the
date and time specified by the arguments.
Packages This Package Prev Next Index
Java API Document (HTML generated by dkramer on April 22, 1996)
Copyright © 1996 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
All rights reserved
Please send any comments or corrections to doug.kramer@sun.com
 is represented by the integer
is represented by the integer 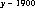 .
.
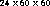 = 86400 seconds in all cases.
In UTC, however, about once every year or two there is an extra second, called a "leap
second." The leap second is always added as the last second of the day, and always on
December 31 or June 30. For example, the last minute of the year 1995 was 61 seconds
long, thanks to an added leap second. Most computer clocks are not accurate enough to be
able to reflect the leap-second distinction.
= 86400 seconds in all cases.
In UTC, however, about once every year or two there is an extra second, called a "leap
second." The leap second is always added as the last second of the day, and always on
December 31 or June 30. For example, the last minute of the year 1995 was 61 seconds
long, thanks to an added leap second. Most computer clocks are not accurate enough to be
able to reflect the leap-second distinction.
 is represented by the integer
is represented by the integer 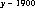 .
.